|
The cation of carbon dioxide, CO+, was definitively detected by
Latter et al. along two sight lines, the molecular
cloud M17SW and the
planetary nebula
NGC 7027, as reported in a 1993 publication. The observations were
made with the 12 m telescope at
Kitt Peak National Observatory. A report from
a decade earlier of the detection of CO+ toward the Orion Molecular Cloud by
Erickson et al. has been discounted: another species is
likely responsible for the single line the paper assigned to CO+.
Since CO+ is thought to be formed by ionizing
CO with high energy photons,
it is considered to be a good tracer of
photon dominated regions and has also been detected
toward PDRs such as
NGC 7023 and the
Orion Bar. CO+ has also been
detected toward
M82, the
Cigar galaxy, following a tentative
detection toward
Cygnus A.
|
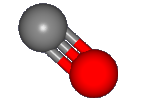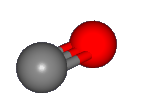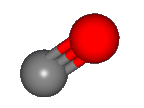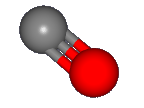
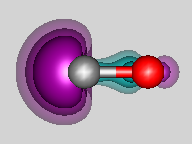
When CO is ionized to form CO+, the electron that is removed comes from the
C 2s orbital, which is pushed away from the C nucleus by the other electrons on the C-O bond axies as shown in
the figure.
|
|
|